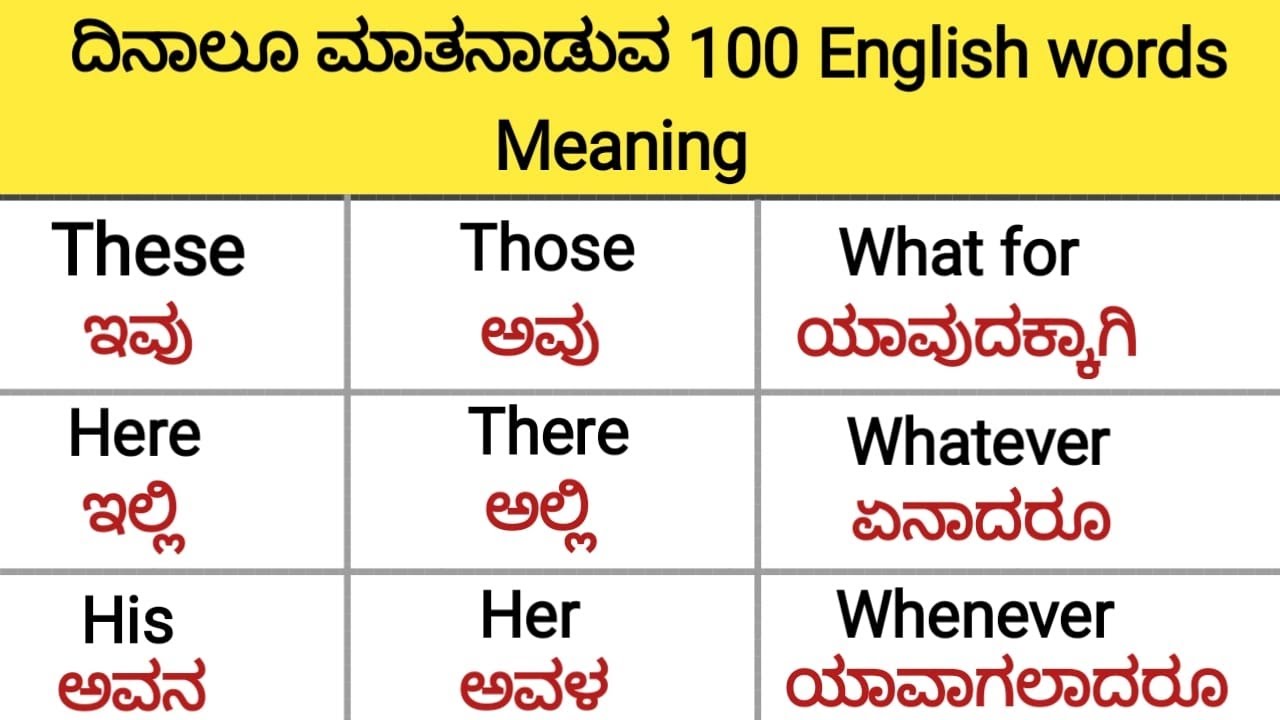
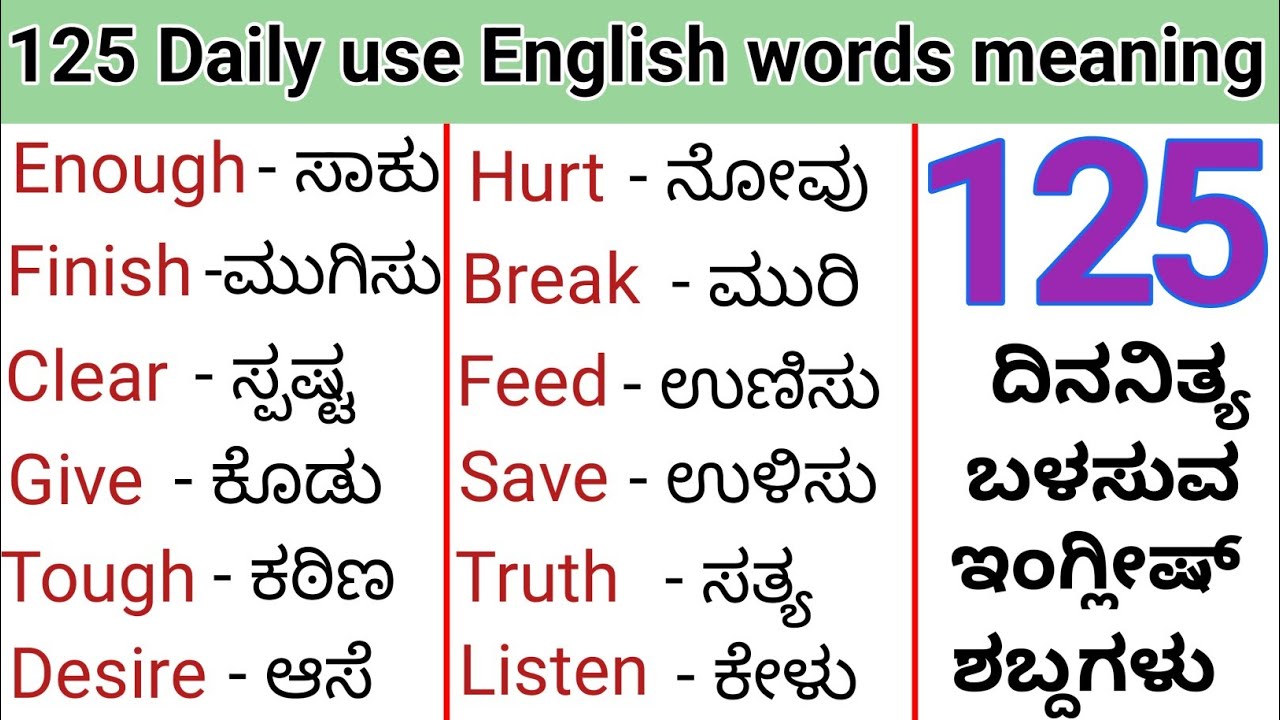
Reflection is a fascinating concept that holds different meanings across various cultures and languages. In the context of Kannada, a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the southwestern region of India, reflection encompasses a rich tapestry of interpretations. It is not merely a literal mirror image but a profound contemplation of thoughts, actions, and emotions. Understanding the reflection meaning in Kannada can offer a unique perspective on how people perceive themselves and the world around them.
The essence of reflection in Kannada is deeply intertwined with the cultural and philosophical heritage of Karnataka, the region where Kannada is primarily spoken. It represents a journey of introspection and self-awareness that transcends the physical realm. In Kannada, reflection is often associated with the idea of 'Chintana' or deep contemplation, which is a vital aspect of spiritual and personal growth. This introspective practice encourages individuals to ponder over their experiences, learn from them, and seek a deeper understanding of their existence.
Moreover, reflection in Kannada also signifies the act of mirroring or reproducing an image, sound, or light. This dual nature of reflection highlights its versatility and significance in everyday life as well as in philosophical discourse. By delving into the reflection meaning in Kannada, one can appreciate how this concept shapes the worldview of Kannada speakers and contributes to their cultural identity. This article explores the multifaceted nature of reflection in Kannada, providing valuable insights into its meanings, applications, and impact on personal and societal levels.
Table of Contents
- What is the Reflection Meaning in Kannada?
- Historical Significance of Reflection in Kannada Culture
- How Does Reflection Influence Kannada Literature and Art?
- The Role of Reflection in Kannada Philosophy and Spirituality
- Reflection in Kannada Education and Learning
- How is Reflection Used in Kannada Music and Theater?
- Reflection in Kannada Language and Communication
- What are the Different Types of Reflection in Kannada?
- Reflection Meaning in Kannada in Everyday Life
- The Impact of Reflection on Personal Development in Kannada Context
- How Reflection Shapes Kannada Societal Values?
- Reflection in Kannada and Modern Technological Advancements
- Future Perspectives of Reflection in Kannada Culture
- Frequently Asked Questions About Reflection in Kannada
- Conclusion
What is the Reflection Meaning in Kannada?
The term 'reflection' in Kannada can be translated as "ಪ್ರತಿಬಿಂಬ" (Pratibimba), which signifies both a physical mirror image and a metaphorical introspection. The dual nature of this term highlights its diverse applications in both tangible and intangible contexts. In Kannada, reflection is not limited to the visual reproduction of an image but extends to the realm of thoughts and emotions.
In a philosophical context, reflection in Kannada involves a process of deep thinking or 'chintana,' where individuals engage in self-analysis and evaluation. This practice is considered crucial for personal growth and spiritual enlightenment. By reflecting on their actions, thoughts, and emotions, individuals can gain valuable insights into their behavior patterns, motivations, and life choices.
Moreover, reflection in Kannada also emphasizes the importance of learning from past experiences. It encourages individuals to analyze their successes and failures, thereby facilitating continuous learning and improvement. This reflective practice is deeply ingrained in the Kannada-speaking community, shaping their approach to life and decision-making processes.
Historical Significance of Reflection in Kannada Culture
Kannada culture, with its rich historical and cultural heritage, places a significant emphasis on reflection as a means of preserving and transmitting knowledge. Historically, reflection has played a crucial role in shaping the philosophical and spiritual traditions of Karnataka. The ancient texts and scriptures of Kannada literature often incorporate themes of reflection and introspection, highlighting their importance in the quest for knowledge and understanding.
Reflection has been a vital element in the teachings of renowned Kannada philosophers and saints, who advocated for self-awareness and contemplative practices as a path to spiritual enlightenment. The works of influential figures like Basaveshwara, Akka Mahadevi, and Allama Prabhu emphasize the importance of reflection in achieving a harmonious balance between the material and spiritual realms.
In addition to its philosophical significance, reflection has also played a pivotal role in the development of Kannada art and literature. The process of reflecting on cultural and historical experiences has inspired countless artists and writers, leading to the creation of timeless masterpieces that continue to resonate with audiences today.
How Does Reflection Influence Kannada Literature and Art?
Reflection has been a driving force behind the evolution of Kannada literature and art, shaping the themes, styles, and narratives that characterize these creative expressions. Kannada literature, with its extensive repertoire of poetry, prose, and drama, often delves into the depths of human emotions, thoughts, and experiences, offering a reflective lens through which readers can explore the complexities of life.
Renowned Kannada literary works, such as those by Kuvempu, Bendre, and Shivaram Karanth, often incorporate elements of reflection and introspection. These authors skillfully weave introspective themes into their narratives, encouraging readers to engage in self-reflection and contemplation. Through their works, they explore the intricacies of human relationships, societal norms, and existential dilemmas, prompting readers to question, analyze, and reflect on their own lives.
In the realm of art, reflection manifests in various forms, from traditional paintings and sculptures to modern installations and performances. Kannada artists often draw inspiration from their cultural heritage, incorporating reflective elements that pay homage to their roots while simultaneously exploring contemporary themes. This fusion of tradition and modernity allows artists to create thought-provoking works that resonate with diverse audiences, fostering a deeper understanding of Kannada culture and identity.
The Role of Reflection in Kannada Philosophy and Spirituality
Reflection holds a significant place in the philosophical and spiritual traditions of Kannada culture, serving as a foundational element in the pursuit of wisdom and enlightenment. Kannada philosophy, influenced by ancient Indian traditions such as Vedanta, Jainism, and Buddhism, emphasizes the importance of self-reflection and introspection in the quest for truth and self-realization.
The practice of reflection is deeply rooted in the teachings of Kannada saints and philosophers, who advocated for a contemplative approach to life. Through reflection, individuals can gain insights into their true nature, uncovering the underlying truths that govern their existence. This introspective journey often involves questioning one's beliefs, values, and assumptions, leading to a more profound understanding of the self and the universe.
In the spiritual realm, reflection is considered a vital tool for achieving inner peace and harmony. By engaging in reflective practices, individuals can cultivate a sense of mindfulness and awareness, enabling them to navigate the challenges of life with equanimity and grace. This reflective approach is integral to Kannada spirituality, guiding individuals on their path to self-discovery and transcendence.
Reflection in Kannada Education and Learning
Reflection is an essential component of the educational process in Kannada-speaking regions, playing a crucial role in fostering critical thinking, creativity, and personal growth. In the context of education, reflection involves the process of analyzing and evaluating one's learning experiences, enabling students to gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and their own learning processes.
Kannada educators often incorporate reflective practices into their teaching methodologies, encouraging students to engage in self-assessment and introspection. By reflecting on their learning experiences, students can identify their strengths and weaknesses, develop problem-solving skills, and enhance their ability to think critically and independently.
Furthermore, reflection in education extends beyond the classroom, influencing the overall development of students as individuals. Through reflective practices, students can cultivate a sense of self-awareness and empathy, enabling them to navigate the complexities of life with confidence and resilience. This holistic approach to education is deeply ingrained in Kannada culture, reflecting the community's commitment to nurturing well-rounded individuals who can contribute positively to society.
How is Reflection Used in Kannada Music and Theater?
Reflection plays a pivotal role in Kannada music and theater, serving as a source of inspiration and creativity for artists and performers. In the realm of music, reflection manifests in the form of lyrics, melodies, and compositions that evoke a sense of introspection and contemplation. Kannada musicians often draw from their cultural and personal experiences, creating reflective works that resonate with audiences on a profound level.
Similarly, Kannada theater often incorporates themes of reflection and introspection, exploring the complexities of human emotions, relationships, and societal issues. Through the medium of theater, playwrights and performers can delve into the depths of the human psyche, offering audiences a reflective lens through which they can examine their own lives and experiences.
This reflective approach to music and theater not only enriches the artistic landscape of Kannada culture but also fosters a deeper connection between performers and audiences. By engaging with reflective themes and narratives, audiences can gain valuable insights into the human condition, promoting empathy, understanding, and personal growth.
Reflection in Kannada Language and Communication
The concept of reflection is deeply embedded in the Kannada language, influencing the way individuals communicate and express themselves. In Kannada, reflection is often associated with the idea of 'pratibimba,' which signifies both a literal mirror image and a metaphorical introspection. This dual nature of reflection highlights its significance in both verbal and non-verbal communication.
In verbal communication, reflection manifests through the use of idiomatic expressions, metaphors, and analogies that encourage introspection and contemplation. Kannada speakers often employ reflective language to convey complex emotions, thoughts, and ideas, enabling them to communicate with depth and nuance.
Non-verbal communication in Kannada culture also incorporates elements of reflection, with gestures, facial expressions, and body language often conveying reflective meanings. This emphasis on reflective communication fosters a deeper understanding and connection between individuals, enhancing the overall quality of interpersonal interactions.
What are the Different Types of Reflection in Kannada?
Reflection in Kannada encompasses a wide range of interpretations and applications, each with its unique significance and impact. Broadly speaking, reflection can be categorized into two primary types: physical reflection and metaphorical reflection.
- Physical Reflection: This type of reflection refers to the literal reproduction of an image, sound, or light. In Kannada, physical reflection is often associated with the concept of 'pratibimba,' which denotes a mirror image or a reflected sound. This type of reflection is commonly observed in everyday life, such as in mirrors, water surfaces, and echoes.
- Metaphorical Reflection: Metaphorical reflection involves the process of introspection and contemplation, where individuals engage in self-analysis and evaluation. This type of reflection is often associated with the concept of 'chintana,' which signifies deep thinking and contemplation. Metaphorical reflection is considered an essential aspect of personal growth and spiritual development in Kannada culture.
Both types of reflection play a crucial role in shaping the way individuals perceive themselves and the world around them, contributing to their cultural identity and worldview.
Reflection Meaning in Kannada in Everyday Life
Reflection is an integral part of everyday life for Kannada speakers, influencing their thoughts, actions, and interactions. In a practical sense, reflection often manifests in the form of self-assessment and introspection, where individuals evaluate their experiences, learn from them, and make informed decisions.
In personal relationships, reflection fosters empathy and understanding, enabling individuals to connect with others on a deeper level. By reflecting on their interactions and experiences, individuals can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of their relationships, enhancing their ability to communicate and collaborate effectively.
Moreover, reflection in everyday life extends to the realm of personal development, where individuals engage in continuous learning and self-improvement. Through reflective practices, individuals can identify their strengths and weaknesses, set meaningful goals, and chart a path towards personal and professional growth.
The Impact of Reflection on Personal Development in Kannada Context
Reflection plays a pivotal role in personal development within the Kannada-speaking community, serving as a catalyst for self-awareness, growth, and transformation. By engaging in reflective practices, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, enabling them to make conscious choices and take proactive steps towards their goals.
In the Kannada context, reflection is often associated with the concept of 'manana,' which signifies the process of internalizing and assimilating knowledge and experiences. Through 'manana,' individuals can integrate their learnings into their daily lives, fostering a sense of coherence and alignment between their values, actions, and aspirations.
Furthermore, reflection in personal development extends to the realm of emotional intelligence, where individuals cultivate the ability to recognize and regulate their emotions. By reflecting on their emotional responses and triggers, individuals can develop greater self-control, empathy, and resilience, enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life.
How Reflection Shapes Kannada Societal Values?
Reflection is a fundamental aspect of Kannada societal values, influencing the way individuals perceive, interpret, and respond to the world around them. In Kannada culture, reflection is often associated with the principles of 'samskara' (cultural refinement) and 'dharma' (righteousness), which emphasize the importance of ethical conduct, social responsibility, and moral integrity.
Through reflective practices, individuals can align their actions with these core values, fostering a sense of community and collective well-being. This emphasis on reflection and introspection encourages individuals to consider the impact of their actions on others and the environment, promoting a culture of empathy, compassion, and mutual respect.
Moreover, reflection in Kannada society extends to the realm of social justice and equity, where individuals are encouraged to challenge societal norms and advocate for change. By reflecting on issues of inequality and injustice, individuals can contribute to the creation of a more inclusive and equitable society, in line with the values of Kannada culture.
Reflection in Kannada and Modern Technological Advancements
In the context of modern technological advancements, reflection continues to play a crucial role in shaping the way Kannada speakers engage with technology and digital media. As technology becomes increasingly integrated into daily life, reflective practices can help individuals navigate the complexities of the digital age with mindfulness and intention.
Reflection in Kannada culture encourages individuals to critically evaluate their use of technology, considering its impact on their well-being, relationships, and the environment. By engaging in reflective practices, individuals can make informed decisions about their technology use, balancing the benefits of digital connectivity with the need for offline presence and interaction.
Furthermore, reflection in the digital age extends to the realm of digital literacy and media consumption, where individuals are encouraged to critically analyze the information they encounter online. Through reflective practices, individuals can develop the skills necessary to navigate the digital landscape with discernment, fostering a culture of informed and responsible digital citizenship.
Future Perspectives of Reflection in Kannada Culture
As Kannada culture continues to evolve in response to global influences and technological advancements, the concept of reflection remains a vital aspect of its identity and values. Looking to the future, reflection is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the cultural landscape of Kannada-speaking communities.
In the realm of education, reflection is expected to become an integral component of teaching and learning methodologies, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and personal growth. As educators continue to explore innovative approaches to education, reflective practices are likely to be incorporated into curricula, enhancing students' ability to engage with complex ideas and challenges.
In the sphere of art and literature, reflection is anticipated to inspire new forms of creative expression, as artists and writers draw from their cultural heritage while embracing contemporary themes and techniques. This fusion of tradition and modernity is expected to enrich the artistic landscape of Kannada culture, fostering a deeper connection between creators and audiences.
Moreover, reflection is likely to continue shaping societal values and norms, as individuals and communities engage in ongoing dialogues about issues of equity, justice, and sustainability. By fostering a culture of reflection and introspection, Kannada-speaking communities can navigate the challenges of the future with resilience, empathy, and a commitment to collective well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions About Reflection in Kannada
1. What is the significance of reflection in Kannada culture?
Reflection in Kannada culture is significant as it encompasses both introspective contemplation and the literal reproduction of images, sounds, or light. It plays a crucial role in personal growth, philosophical discourse, art, literature, and societal values.
2. How does reflection influence Kannada literature?
Reflection influences Kannada literature by shaping themes, styles, and narratives. It encourages introspection and exploration of human emotions, relationships, and societal issues, prompting readers to engage in self-reflection and contemplation.
3. What role does reflection play in Kannada education?
Reflection in Kannada education fosters critical thinking, creativity, and personal growth. It involves self-assessment and introspection, enabling students to gain a deeper understanding of their learning processes and develop problem-solving skills.
4. How is reflection used in Kannada music and theater?
Reflection in Kannada music and theater serves as a source of inspiration and creativity. It manifests in the form of lyrics, melodies, and narratives that evoke introspection and contemplation, fostering a deeper connection between performers and audiences.
5. What are the different types of reflection in Kannada?
In Kannada, reflection can be categorized into physical reflection (literal reproduction of images, sounds, or light) and metaphorical reflection (introspection and contemplation). Both types play a crucial role in shaping perceptions and cultural identity.
6. How does reflection shape Kannada societal values?
Reflection shapes Kannada societal values by promoting ethical conduct, social responsibility, and moral integrity. It encourages individuals to consider the impact of their actions on others and the environment, fostering a culture of empathy and mutual respect.
Conclusion
The concept of reflection in Kannada is a multifaceted one, encompassing both physical and metaphorical interpretations. It holds significant cultural, philosophical, and practical implications, influencing various aspects of life including art, literature, education, and societal values. Through reflection, Kannada-speaking individuals can engage in introspection, self-assessment, and learning, fostering personal growth and spiritual development. As Kannada culture continues to evolve, reflection remains a vital component of its identity, offering valuable insights and perspectives that enrich the human experience. By embracing reflective practices, individuals and communities can navigate the complexities of life with mindfulness, empathy, and a commitment to collective well-being.
You Might Also Like
The World Of Kerry Washington's Kids: A Closer LookHannah Uwu Of Pics: Your Ultimate Guide
All About Yoo Yeon-Seok Wife: A Deep Dive Into Personal And Professional Life
Gry Park Actress: A Star's Journey In The World Of Cinema
Meet Jo Jung Suk's Wife: A Closer Look At Her Life And Achievements
Article Recommendations