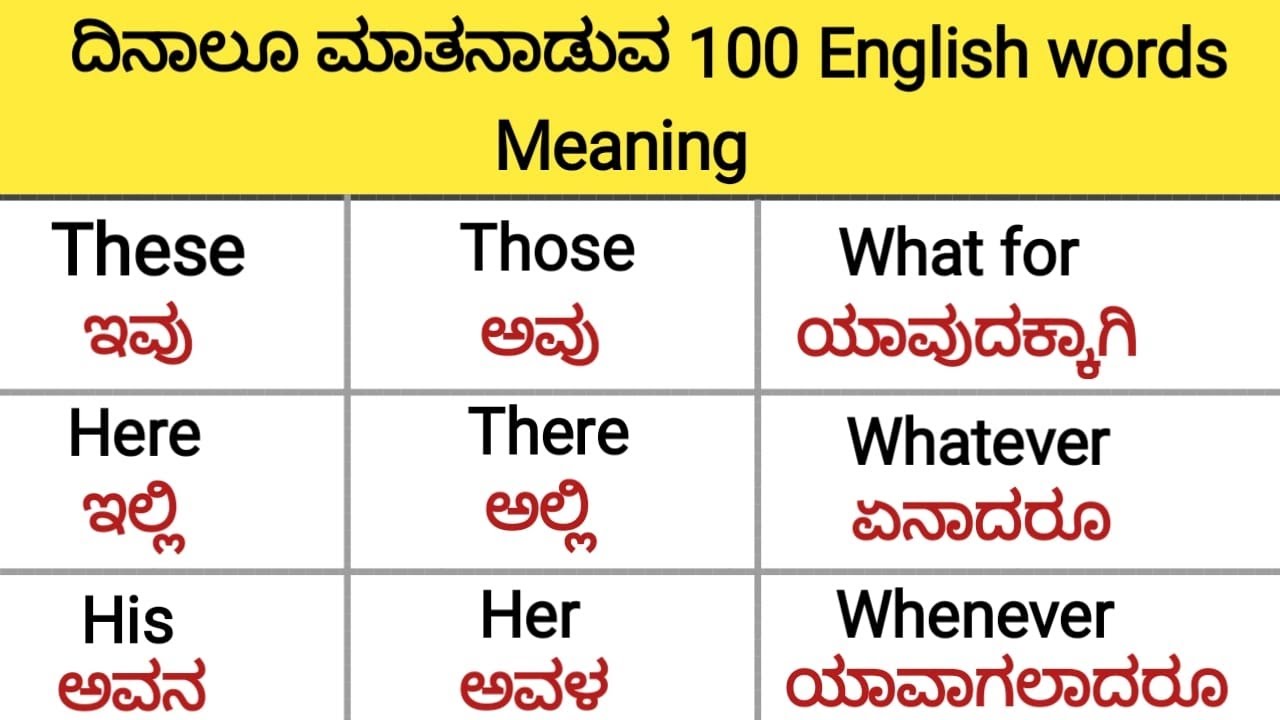
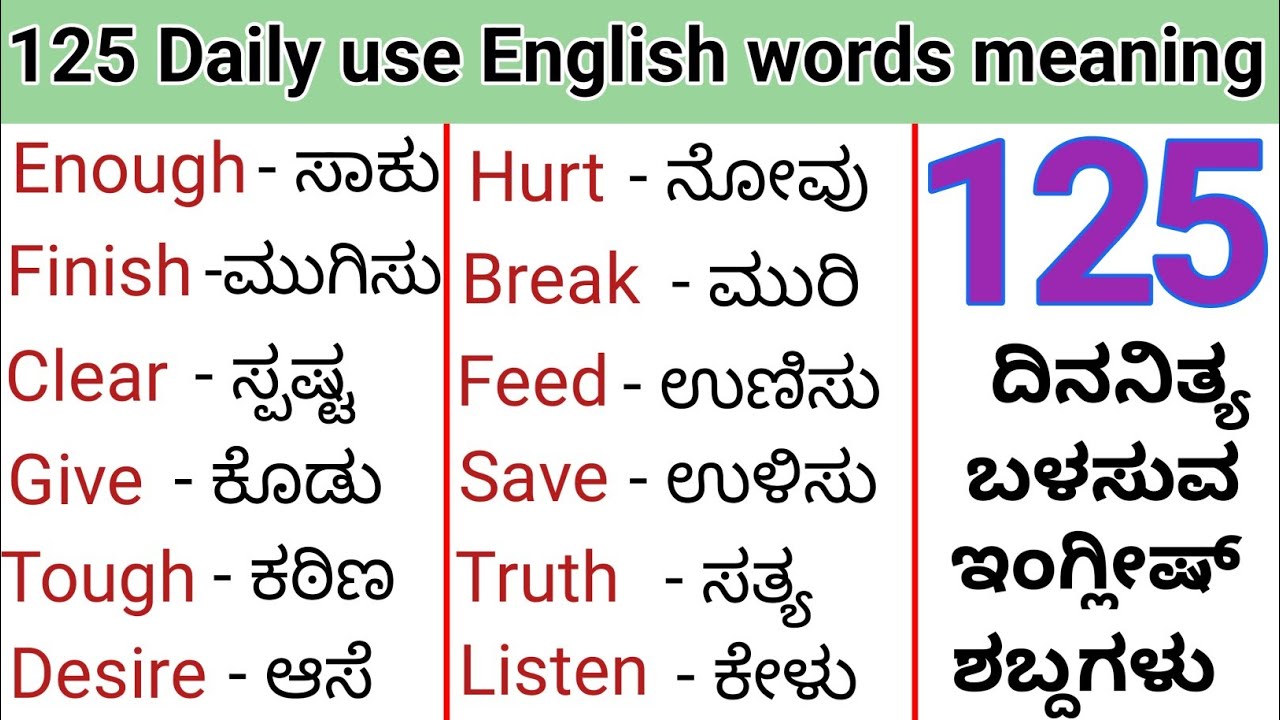
The Kannada language, one of the rich Dravidian languages, boasts a profound cultural heritage and linguistic complexity that dates back over two millennia. An essential part of India's linguistic tapestry, Kannada is the official language of the state of Karnataka and holds a special place in the hearts of its speakers. For those looking to "explore meaning in kannada," understanding this language involves delving into its historical context, literary contributions, and its role in the modern world.
Known for its classical status, Kannada has a rich literary tradition, with contributions spanning poetry, drama, and prose. The language has evolved through various stages, from Old Kannada in the early centuries to its modern form today. As a Dravidian language, Kannada shares similarities with Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam, yet it retains its unique identity through distinct phonetic sounds, script, and grammar. With over 40 million native speakers, Kannada continues to thrive, adapting to contemporary challenges while preserving its traditional roots.
In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey through the Kannada language, exploring its historical development, cultural significance, and the nuances that make it both fascinating and complex. We will also provide practical insights for those interested in learning Kannada, including linguistic features, common phrases, and tips on improving proficiency. Whether you're a language enthusiast or a cultural explorer, this guide will offer valuable insights to deepen your understanding of Kannada and its enduring legacy.
Table of Contents
- Origin and History of Kannada
- What is the Script of Kannada?
- How Did Kannada Evolve Over Time?
- Influence of Sanskrit on Kannada
- Dialects and Regional Variations
- Kannada Literature and Its Impact
- Famous Kannada Authors and Poets
- Cultural Significance of Kannada
- How is Kannada Used in Modern Media?
- Learning Kannada: Tips and Tricks
- Common Kannada Phrases and Words
- How Does Kannada Compare to Other Dravidian Languages?
- The Future of Kannada Language
- Explore Meaning in Kannada
- FAQs About Kannada Language
Origin and History of Kannada
The origins of the Kannada language can be traced back to the early centuries of the Common Era. As a member of the Dravidian language family, Kannada shares its roots with other South Indian languages like Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam. The earliest inscriptions in Kannada date back to the 5th century, highlighting its long-standing presence.
Kannada's development is usually divided into three distinct periods: Old Kannada (450-1200 CE), Middle Kannada (1200-1700 CE), and Modern Kannada (1700 CE onward). Each phase reflects significant linguistic and cultural transformations influenced by various dynasties, including the Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and Vijayanagara Empire, which patronized Kannada literature and arts.
What is the Script of Kannada?
The Kannada script is an abugida, which means that each character represents a consonant with an inherent vowel sound. It evolved from the Kadamba script, which in turn was derived from the Brahmi script of ancient India. The script is known for its round shapes and unique diacritics that modify the base consonant sounds.
Kannada script consists of 49 characters, including 13 vowels and 36 consonants. The script is used not only for writing Kannada but also by other languages such as Tulu, Konkani, and Kodava. Its visual appeal and phonetic richness make it a distinctive feature of the language.
How Did Kannada Evolve Over Time?
The evolution of Kannada over time is a fascinating journey marked by linguistic adaptations and external influences. During the Old Kannada period, the language was primarily used for inscriptions and religious texts. The Middle Kannada period saw the emergence of significant literary works, including the famous "Vachana Sahitya" by Basavanna and his contemporaries.
Modern Kannada began to take shape in the 18th century, incorporating elements from other languages due to increased interactions. This period was marked by the rise of prose literature and the consolidation of the language's grammar and vocabulary, paving the way for its contemporary form.
Influence of Sanskrit on Kannada
Sanskrit has had a profound impact on Kannada, enriching its vocabulary and literary traditions. During the medieval period, Kannada literature witnessed a significant Sanskritization, with numerous works being composed in a mix of Kannada and Sanskrit, known as "Sanskritized Kannada."
This influence is evident in the language's lexicon, where many technical, religious, and philosophical terms are borrowed from Sanskrit. Additionally, Kannada poets and scholars often drew inspiration from Sanskrit literature, translating and adapting classical texts to cater to Kannada-speaking audiences.
Dialects and Regional Variations
Kannada is characterized by its diverse dialects, which reflect the cultural and geographical diversity of Karnataka. The major dialects include Mysuru Kannada, Bengaluru Kannada, and Dharwad Kannada, each with unique phonetic and lexical features.
These regional variations can be attributed to historical migrations, trade, and cultural exchanges. Despite these differences, Standard Kannada serves as the lingua franca, ensuring mutual intelligibility among speakers across the state.
Kannada Literature and Its Impact
Kannada literature boasts a rich tradition that spans over a thousand years, contributing significantly to Indian literary heritage. From classical works like "Pampa Bharata" and "Vaddaradhane" to modern novels and poetry, Kannada literature encompasses a wide range of genres and themes.
The literary landscape of Kannada has been shaped by various movements, including the "Navodaya" and "Navya" movements, which brought fresh perspectives and experimental styles. Kannada writers have been recognized with numerous national and international awards, underscoring the language's literary prowess.
Famous Kannada Authors and Poets
Kannada literature is graced by the works of renowned authors and poets who have left an indelible mark on the literary world. Some of the prominent figures include:
- Kuvempu: A celebrated poet and novelist, Kuvempu is known for his epic "Sri Ramayana Darshanam," which won the Jnanpith Award.
- U.R. Ananthamurthy: A leading figure in modern Kannada literature, Ananthamurthy's novel "Samskara" is a landmark in Indian literature.
- P. Lankesh: Known for his sharp socio-political commentary, Lankesh was a prolific writer and journalist.
- Akkamahadevi: A prominent poetess and mystic, Akkamahadevi's "Vachanas" are revered for their spiritual depth.
Cultural Significance of Kannada
Kannada is more than just a language; it is a cultural identity that binds the people of Karnataka. The language plays a pivotal role in preserving and promoting Karnataka's rich cultural heritage, including its music, dance, theatre, and festivals.
Festivals like "Kannada Rajyotsava" celebrate the language's significance, fostering a sense of pride and unity among its speakers. Kannada also serves as a medium for traditional art forms like Yakshagana and Harikathe, ensuring the transmission of cultural values across generations.
How is Kannada Used in Modern Media?
In today's digital age, Kannada has embraced modern media, becoming a vibrant part of television, cinema, and online platforms. Kannada cinema, popularly known as "Sandalwood," produces a wide array of films that reflect contemporary issues and cultural narratives.
The rise of digital media has further expanded Kannada's reach, with numerous websites, blogs, and social media platforms catering to Kannada-speaking audiences. This digital presence has played a crucial role in promoting the language globally.
Learning Kannada: Tips and Tricks
For those interested in learning Kannada, here are some practical tips to enhance your language skills:
- Start with basics: Familiarize yourself with the Kannada script and basic grammar rules.
- Use language apps: Leverage language learning apps and online resources for interactive lessons.
- Practice speaking: Engage with native speakers to improve pronunciation and conversational skills.
- Immerse yourself: Watch Kannada movies, listen to Kannada music, and read Kannada literature to gain exposure.
Common Kannada Phrases and Words
Here are some common Kannada phrases and words to get you started:
- Hello: Namaskara
- Thank you: Dhanyavadagalu
- Yes: Haudu
- No: Illa
- How are you?: Hegiddira?
How Does Kannada Compare to Other Dravidian Languages?
Kannada shares many similarities with other Dravidian languages, such as Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam, yet maintains its distinct characteristics. While these languages share a common ancestry, each has developed unique phonetic, grammatical, and lexical features over time.
Kannada, for example, is known for its use of compound letters and a rich system of honorifics, which add layers of politeness and respect to communication. Despite these differences, mutual intelligibility is possible in certain contexts, especially among speakers familiar with multiple Dravidian languages.
The Future of Kannada Language
The future of the Kannada language looks bright, with concerted efforts to promote and preserve its cultural and linguistic heritage. Initiatives by the government and cultural organizations aim to enhance Kannada's presence in education, technology, and media.
As globalization continues to influence languages worldwide, Kannada remains resilient, adapting to new challenges while retaining its traditional essence. The language's enduring legacy will depend on the continued commitment of its speakers to cherish and propagate its rich heritage.
Explore Meaning in Kannada
To "explore meaning in kannada" is to delve into a language that encapsulates a rich tapestry of history, culture, and linguistic beauty. Kannada provides a window into the soul of Karnataka, offering insights into its people's way of life, beliefs, and traditions.
Understanding Kannada goes beyond mere translation; it involves appreciating the nuances and subtleties that give the language its depth and vibrancy. For language enthusiasts, Kannada offers a rewarding experience, revealing the interconnectedness of language and culture.
FAQs About Kannada Language
1. Is Kannada a difficult language to learn?
While Kannada has its complexities, especially in terms of script and grammar, it is relatively easy to learn with consistent practice and exposure. Language learning apps and resources can greatly assist new learners.
2. How many people speak Kannada?
Kannada is spoken by over 40 million people, primarily in the state of Karnataka, with smaller communities in neighboring states and abroad.
3. What is the official status of Kannada in India?
Kannada is the official language of Karnataka and one of the 22 scheduled languages recognized by the Indian Constitution.
4. Are there any Kannada language certifications?
Yes, various institutions offer certifications in Kannada language proficiency, which can be beneficial for academic and professional purposes.
5. How can I improve my Kannada vocabulary?
To enhance vocabulary, immerse yourself in Kannada media, read Kannada literature, and practice with native speakers regularly.
6. What are some popular Kannada films I should watch?
Some popular Kannada films include "Mungaru Male," "KGF," "Kirik Party," and "Lucia," which offer a glimpse into Kannada cinema and culture.
The Kannada language, with its rich history and cultural significance, continues to thrive and evolve in the modern world. By understanding its nuances and embracing its beauty, learners and speakers alike contribute to preserving its legacy for future generations.
You Might Also Like
Revolutionize Your Garden With The Highest Yielding Autoflower 2024Reviving The Essence Of A Sad Renew Demise: A Comprehensive Guide
Struggle Meaning In Kannada: Insights Into Life's Challenges
Intriguing Aspects Of Erosme: A Detailed Examination
In-Depth Look At Indian Ullu Webseries: A Cultural Phenomenon
Article Recommendations